概念
什么是循环引用?
故名思义,多个对象形成环路。
有哪几种循环引用?
在Spring中存在如下几种循环引用,一一举例分析一下
- 注入循环引用(
Set注入注解注入)
package c.q.m;import lombok.Data;/** * @Auther: chenqimiao * @Date: 2019/6/28 11:16 * @Description: */@Datapublic class You { private Me me;} package c.q.m;import lombok.Data;/** * @Auther: chenqimiao * @Date: 2019/6/28 11:16 * @Description: */@Datapublic class Me { private You you;} package c.q.m;import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;/** * @Auther: chenqimiao * @Date: 2019/6/28 13:44 * @Description: */public class CircularReferenceTest { @Test public void injectionTest() { BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("circular-reference-beans-test-config.xml")); Me me = beanFactory.getBean(Me.class); You you = beanFactory.getBean(You.class); Assert.assertEquals(me.getYou(), you); }} - 构造器循环引用
package c.q.m;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Getter;/** * @Auther: chenqimiao * @Date: 2019/6/28 11:16 * @Description: */@AllArgsConstructor@Getterpublic class You { private Me me;} package c.q.m;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Getter;/** * @Auther: chenqimiao * @Date: 2019/6/28 11:16 * @Description: */@AllArgsConstructor@Getterpublic class Me { private You you;} package c.q.m;import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;/** * @Auther: chenqimiao * @Date: 2019/6/28 13:44 * @Description: */public class CircularReferenceTest { @Test public void constructorTest() { BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("circular- reference-beans-test-config.xml")); Me me = beanFactory.getBean(Me.class); You you = beanFactory.getBean(You.class); Assert.assertEquals(me.getYou(), you); }} - 工厂构造循环引用(与构造器循环引用类似)
Spring如何解决
提前暴露一个
ObjectFactory类型的工厂对象,通过这种方式Spring解决了单例模式下的注入循环引用,至于其他类型的循环引用Spring也并没有什么好的解决办法。
通过源码的方式来分析一下Spring的手段
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory
protected
T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class requiredType, @Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); } else { // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: // We're assumably within a circular reference. if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) { return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean( nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly); } else if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else if (requiredType != null) { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } else { return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup); } } if (!typeCheckOnly) { markBeanAsCreated(beanName); } try { final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dep : dependsOn) { if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"); } registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); try { getBean(dep); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex); } } } // Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. Object prototypeInstance = null; try { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " + "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } } // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) { try { T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); if (convertedBean == null) { throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } return convertedBean; } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex); } throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } } return (T) bean; } 跟踪上面的
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);方法org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
@Override @Nullable public Object getSingleton(String beanName) { return getSingleton(beanName, true); } @Nullable protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) { Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) { //*******singleFactory中拿到提前暴露的ObjectFactory对象******// ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName); if (singletonFactory != null) { singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); } } } } return singletonObject; }定位到这里,发现Spring再获取bean的时候,会去
singletonFactories集合里面拿一个ObjectFactory对象,再调用其
getObject()方法拿到我们想要的bean.那么问题来了,singletonFactories的对象是何时put进去的?带着这个问题,我们跟踪一下singletonFactories这个集合。我们回到
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory的doGetBean方法,定位到下面的代码段:// Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); }定义的bean是单例,则调用
getSingleton方法,跟踪这个方法发现它是属于org.springframework.beans.factory.suppor.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry 的public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null) { if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) { throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName, "Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " + "(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)"); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } beforeSingletonCreation(beanName); boolean newSingleton = false; boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null); if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>(); } try { singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); newSingleton = true; } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { // Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime -> // if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state. singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null) { throw ex; } } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) { ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException); } } throw ex; } finally { if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { this.suppressedExceptions = null; } afterSingletonCreation(beanName); } if (newSingleton) { addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject); } } return singletonObject; } }这个方法提供了很多的扩展方法,但是我们关注的核心是这一句话
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();而singletonFactory就是我们刚刚传入的函数。try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; }接着定位到
createBean方法,它是属于org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的@Override protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); } RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd; // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and // clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class // which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition. Class resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) { mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd); mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass); } // Prepare method overrides. try { mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides(); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex); } try { // Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); if (bean != null) { return bean; } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex); } try { Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); } return beanInstance; } catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) { // A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already, // or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry. throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex); } }跟踪这一句话
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance(); Class beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass(); if (beanType != NullBean.class) { mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; } // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); } mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); SetactualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; } 真相差不多浮出水面了,请看这一句话
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) { this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory); this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName); } } }this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);就在这里beanFactory被put进了singletonFactories.看一下singletonFactory具体的实现protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) { Object exposedObject = bean; if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName); } } } return exposedObject; }将传入的bean经过BeanPostProcessor的处理后返回。那么传入的bean到底是什么状态的bean呢?
此时的bean是完成了初始化构造的bean,但是还没有进行set或者注解注入的bean,是bean的一个中间状态。
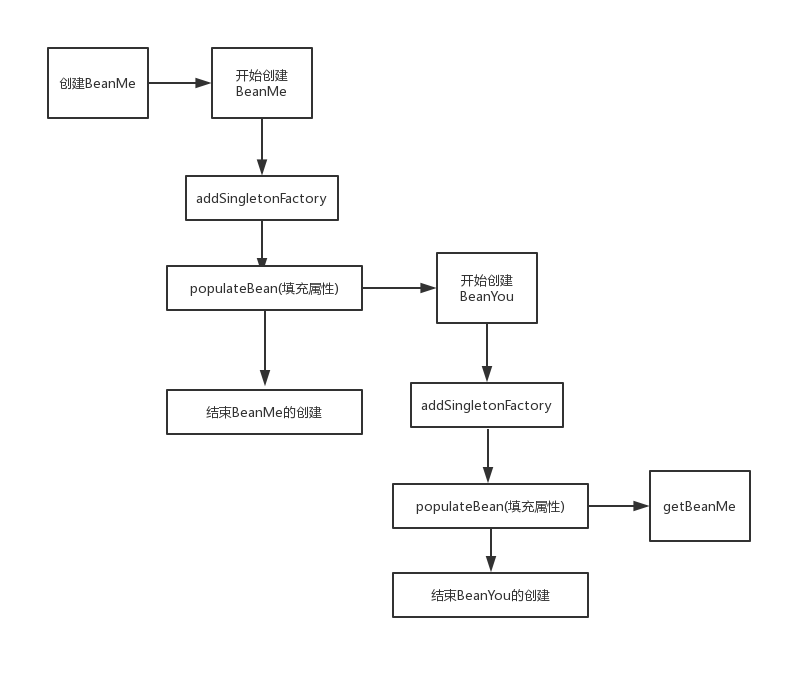
说到这里应该差不多清晰了,Spring会在bean还未完全实例化的时候,将bean包装在ObjectFactory里面,调用
doGetBean的时候,先尝试去ObjectFactory中去拿还未完全实例化的bean.YouandMe的例子在注解注入造成循环依赖时,Spring的调用链时序图如下: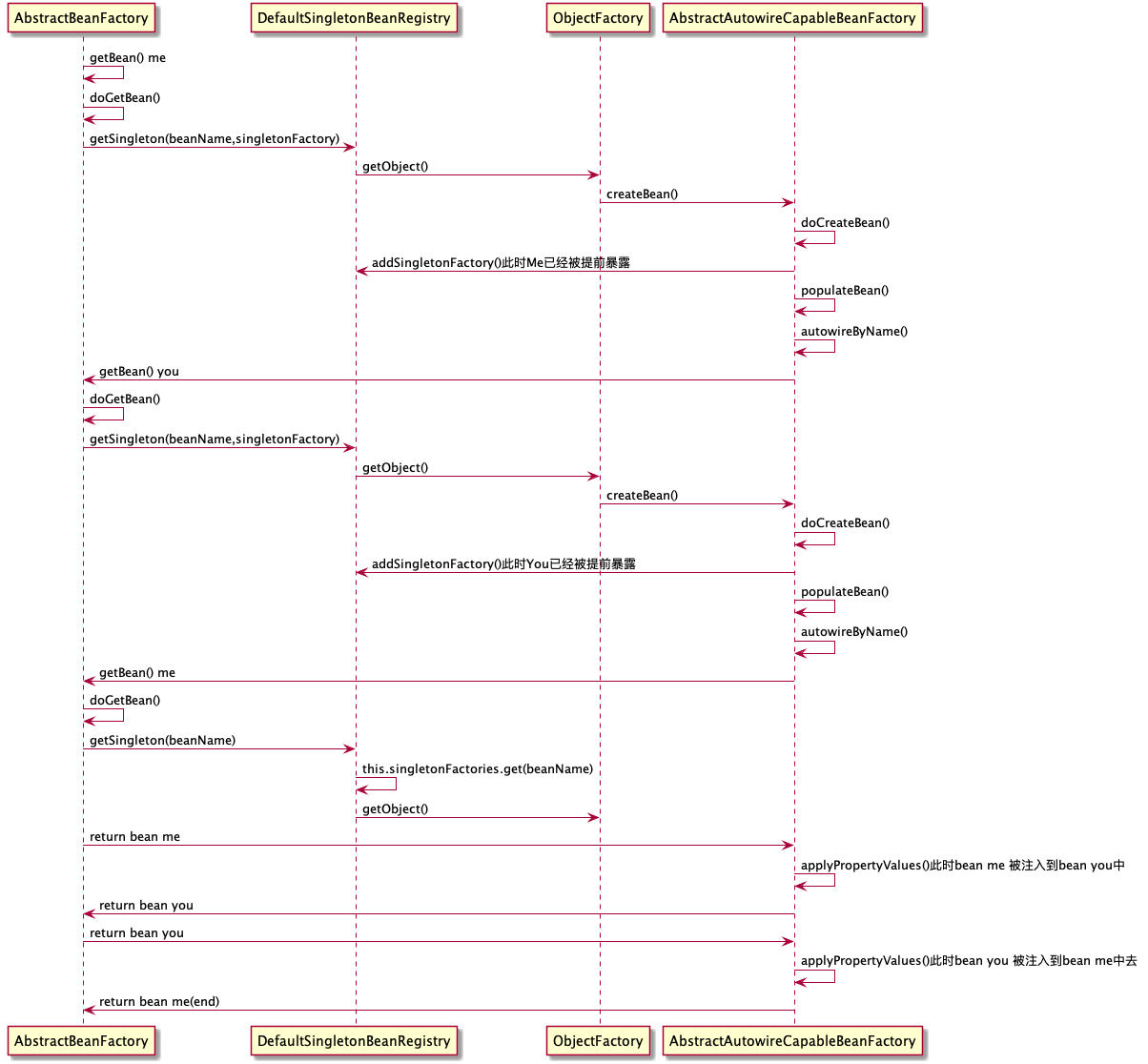
总结